Phone: +44 (0)20 8492 1600
Need help or have a question?
Contact us at: [email protected]
Athlete’s foot, or tinea pedis, is a skin infection caused by a group of fungi known as dermatophytes. Let’s delve deeper into the causes of athlete’s foot and explore the risk factors that make individuals more susceptible to this condition.
Dermatophytes are the primary culprits behind athlete’s foot. These fungi thrive in warm, damp environments such as the insides of shoes, socks, swimming pool decks, locker rooms, and public showers. Given the right conditions, dermatophytes can quickly multiply, leading to an infection.
The fungi responsible for athlete’s foot aren’t restricted to the feet; they cause other forms of tinea (fungal infections), too. For instance, tinea cruris (jock itch) affects the groin area, while tinea corporis (ringworm) can occur anywhere on the body.
The fungi can spread from person to person through direct contact or indirectly through contact with contaminated objects or surfaces. For example, if someone with athlete’s foot walks barefoot in a communal shower, the fungi can linger on the shower floor, ready to infect the next person who walks barefoot in the same area.
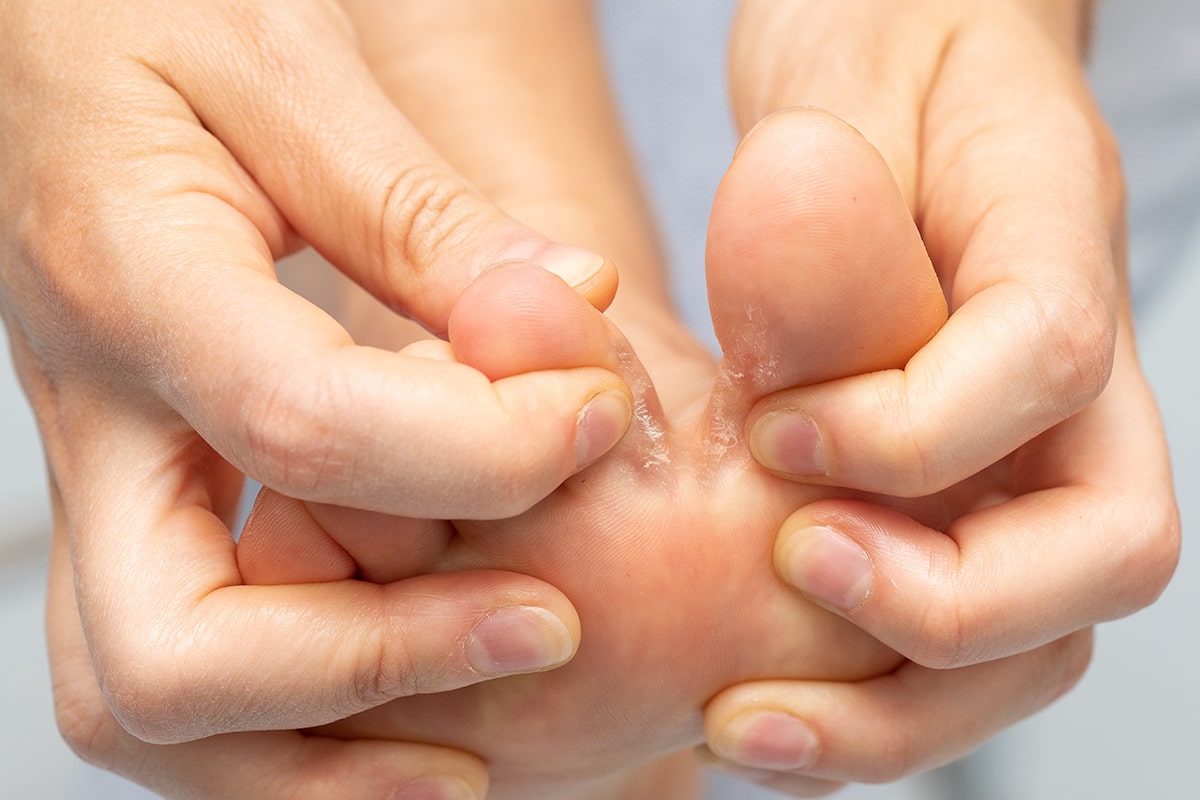
While anyone can get athlete’s foot, certain factors can increase your risk:
Understanding these risk factors can help you take preventative measures to avoid contracting athlete’s foot. By keeping your feet clean and dry, wearing breathable footwear, avoiding sharing personal items, and protecting your feet in public areas, you can significantly reduce your risk of getting this infection.